- Published on
Introduction to AWS Solution Architect Associate
- Authors

- Name
- Kai Do
- @dotrungkien-me
- What is the AWS Cloud?
- Why This Certification Matters
- Exam Structure
- Core AWS Services by Category
- Sample Use Case: 3-Tier Web App on AWS
- What's Next?
Introduction
The AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate certification is designed for individuals who want to design systems that are highly available, cost-efficient, fault-tolerant, and scalable.
This article introduces the certification and lays the foundation for understanding the AWS Cloud, its services, and why cloud architecture matters today.
What is the AWS Cloud?
At its core, the AWS Cloud is a collection of on-demand computing resources and services — such as compute, storage, databases, and networking — delivered over the internet.
☁️ Cloud Advantages
- Pay-as-you-go pricing model
- Scalability on-demand
- Global reach with 32+ regions
- High availability via multi-AZ setups
- Managed infrastructure and automation tools
AWS provides over 200 services across categories like compute, storage, AI/ML, networking, security, DevOps, and analytics.
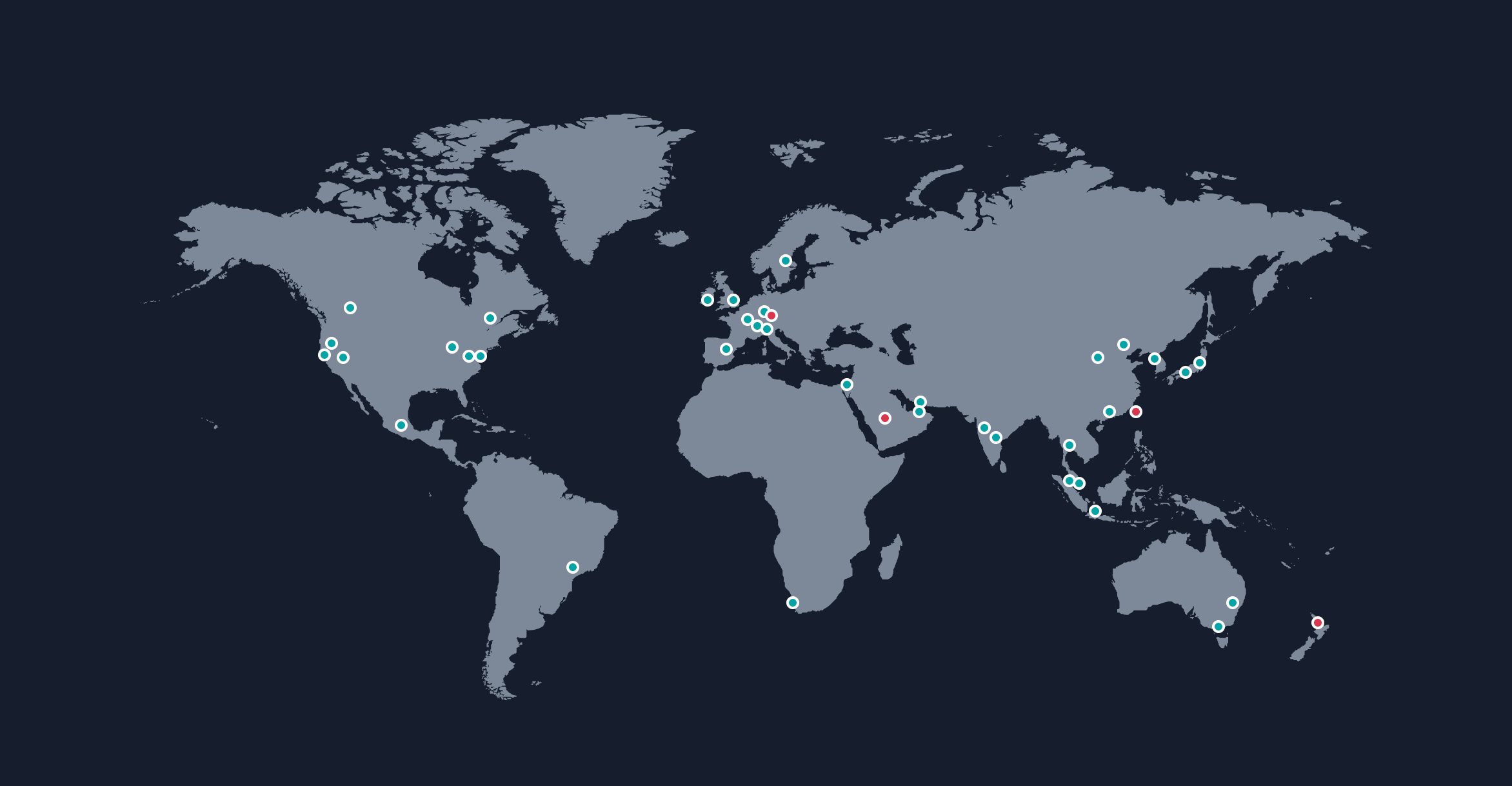
Image: AWS Global Infrastructure - Regions and Availability Zones
Why This Certification Matters
Becoming a certified Solutions Architect means you can:
- Build scalable, reliable cloud-native applications
- Understand trade-offs in design decisions (e.g., S3 vs EBS vs EFS)
- Use security best practices (e.g., IAM roles, KMS, VPC isolation)
- Manage cost with the right pricing models
Exam Structure
| Section | Weight |
|---|---|
| Design Secure Architectures | 30% |
| Design Resilient Architectures | 26% |
| Design High-Performing Architectures | 24% |
| Design Cost-Optimized Architectures | 20% |
Core AWS Services by Category
Below is a quick map of the key services covered on the exam:
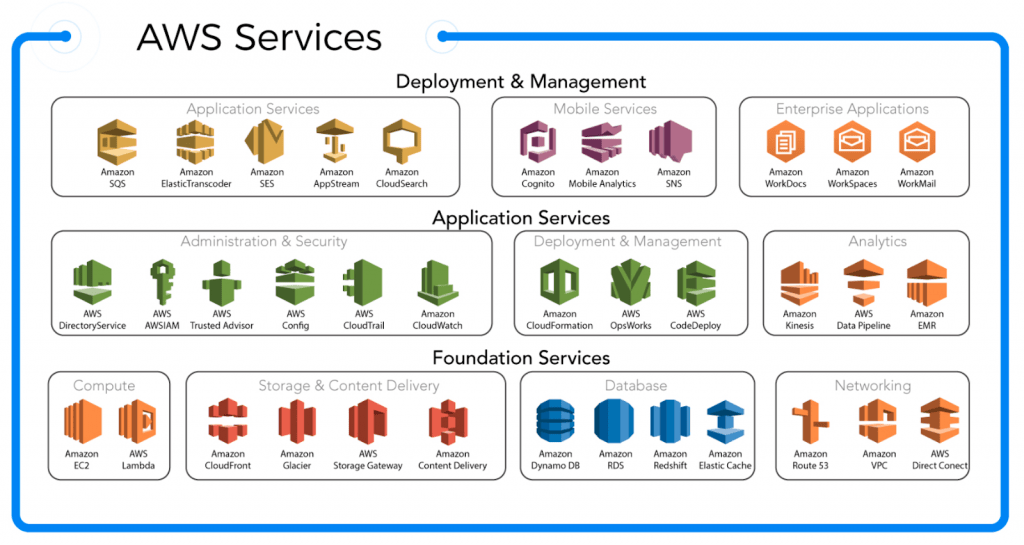
Image: Map of AWS Core Services Categorized (Compute, Storage, Network, Security, Monitoring)
🧠 Compute
- EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)
- Lambda (serverless)
- Elastic Beanstalk
- Auto Scaling
📦 Storage
- S3 (Simple Storage Service)
- EBS (Elastic Block Store)
- EFS (Elastic File System)
- Glacier (for archival)
🌐 Networking
- VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)
- NAT Gateway
- Load Balancers (ALB/NLB)
- Route 53 (DNS)
🔐 Security
- IAM (Users, Roles, Policies)
- KMS (Key Management Service)
- AWS WAF & Shield
- Cognito (user auth)
🧭 Monitoring & Logs
- CloudWatch
- CloudTrail
- AWS Config
- X-Ray
Sample Use Case: 3-Tier Web App on AWS
Here’s a simplified view of how you might build a 3-tier web app architecture using AWS services:
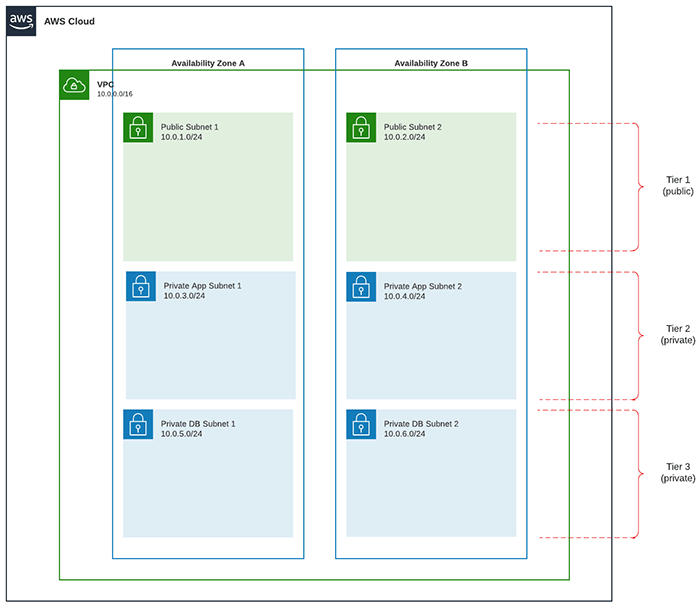
Image: A typical 3-tier architecture using Load Balancer, EC2 instances, RDS database, and public/private subnets
What's Next?
This is the first article in a series that will walk you through everything needed to pass the AWS SAA-C03 exam and become a well-rounded cloud architect.
Next Article → Designing Secure Architectures with IAM, VPC, and Encryption
Questions? Drop a comment below or reach out on GitHub.